No audio available for this content.

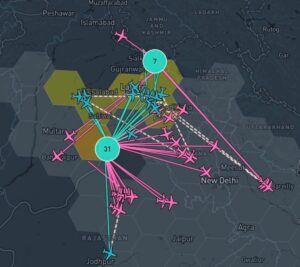
In the current context of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the issue of GNSS jamming and/or possible spoofing has intensified in geographical areas surrounding the conflict zone and other areas, according to the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). The agency issued a safety information bulletin on March 17 warning of a GNSS outage leading to navigation / surveillance degradation. According to the bulletin, which was directed at national aviation authorities and airlines, reports analyzed by EASA indicate that since February 24 GNSS spoofing and/or jamming has intensified in four key geographical areas:
- the Kaliningrad region, surrounding Baltic Sea and neighboring states
- Eastern Finland
- the Black Sea and
- the Eastern Mediterranean area near Cyprus, Turkey, Lebanon, Syria and Israel, as well as Northern Iraq.
“The effects of GNSS jamming and/or possible spoofing,” the bulletin stated, “were observed by aircraft in various phases of their flights, in certain cases leading to re-routing or even to change the destination due to the inability to perform a safe landing procedure.” It pointed out that in the present conditions it is not possible to predict these outages and their effects. Potential issues include:
- loss of ability to use GNSS for waypoint navigation
- loss of area navigation (RNAV) approach capability
- inability to conduct or maintain various operations
- triggering of terrain warnings, possibly with pull-up command and
- inconsistent aircraft position on the navigation display
- loss of automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B), wind shear, terrain and surface functionalities
- failure or degradation of ATM/ANS/CNS and aircraft systems that use GNSS as a time reference and
- airspace infringements and/or route deviations due to GNSS degradation.
The bulletin also offers several recommendations to airlines for mitigating these issues.